656 Artificial Intelligence-Guided Personalized Surgical Planning: Ai-Physician Avatar Assistance In Partial Nephrectomy
Dr. Alberto Piana
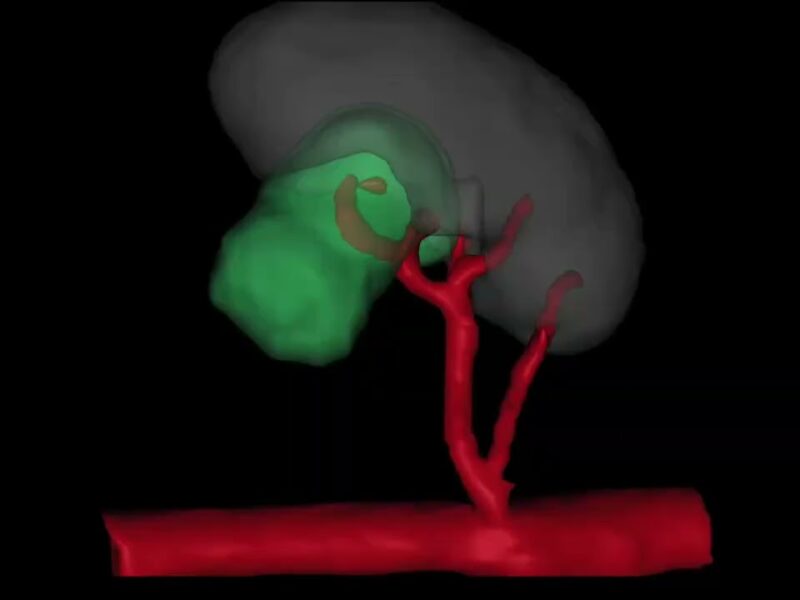
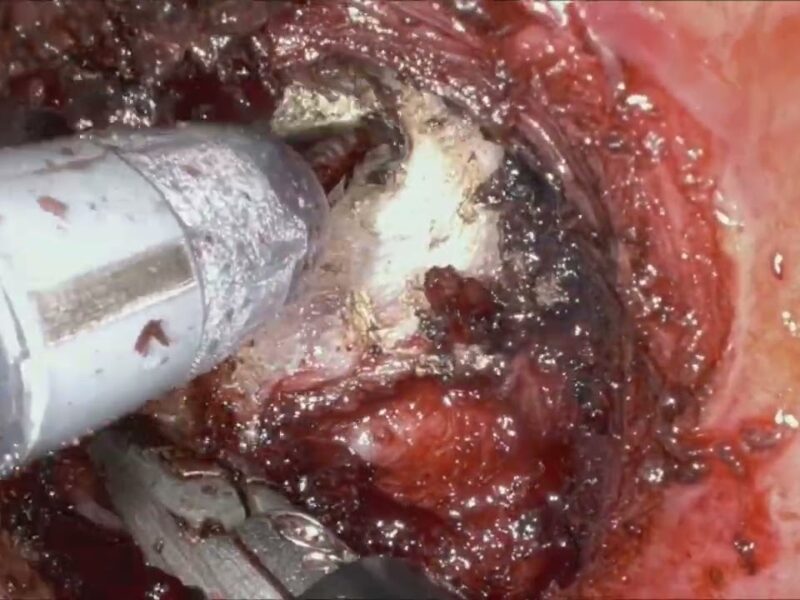
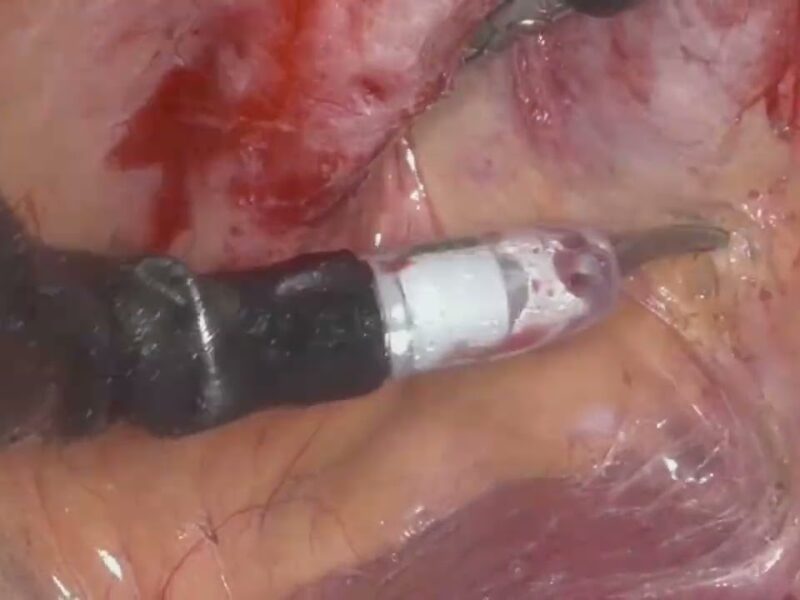
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to transform surgical practice, particularly through predictive algorithms for postoperative outcomes. However, these algorithms often lack user-friendly interfaces for clinician interaction. This study aimed to evaluate an AI-driven model designed to predict the optimal surgical approach for maximizing functional outcomes in patients undergoing robot-assisted partial nephrectomy (RAPN) integrated with a graphical interface that enables direct verbal physician-algorithm interaction.
Technological Innovation, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Robot-assisted partial nephrectomy (RAPN)
See more at: https://vattikutifoundation.com/videos/
Date
August 15, 2020