INTRODUCTION
What are Mumps and What Causes Them?
Mumps is a viral infection caused by a virus called Paramyxovirus. It causes symptoms of viral infection, including fever, fatigue, and muscle pain. This virus infects a pair of salivary glands (parotid glands) found in the cheek, near the ear. Swelling in either of these glands gives people with Mumps virus a prominent swelling of the cheeks. Mumps can infect people of all age groups, but younger adults are most commonly affected by it. Mumps is a highly contagious disease, and it spreads via saliva or respiratory droplets of the infected person. This is called direct transmission of the virus, and anyone close to the infected person is highly likely to contract it as well.
Symptoms
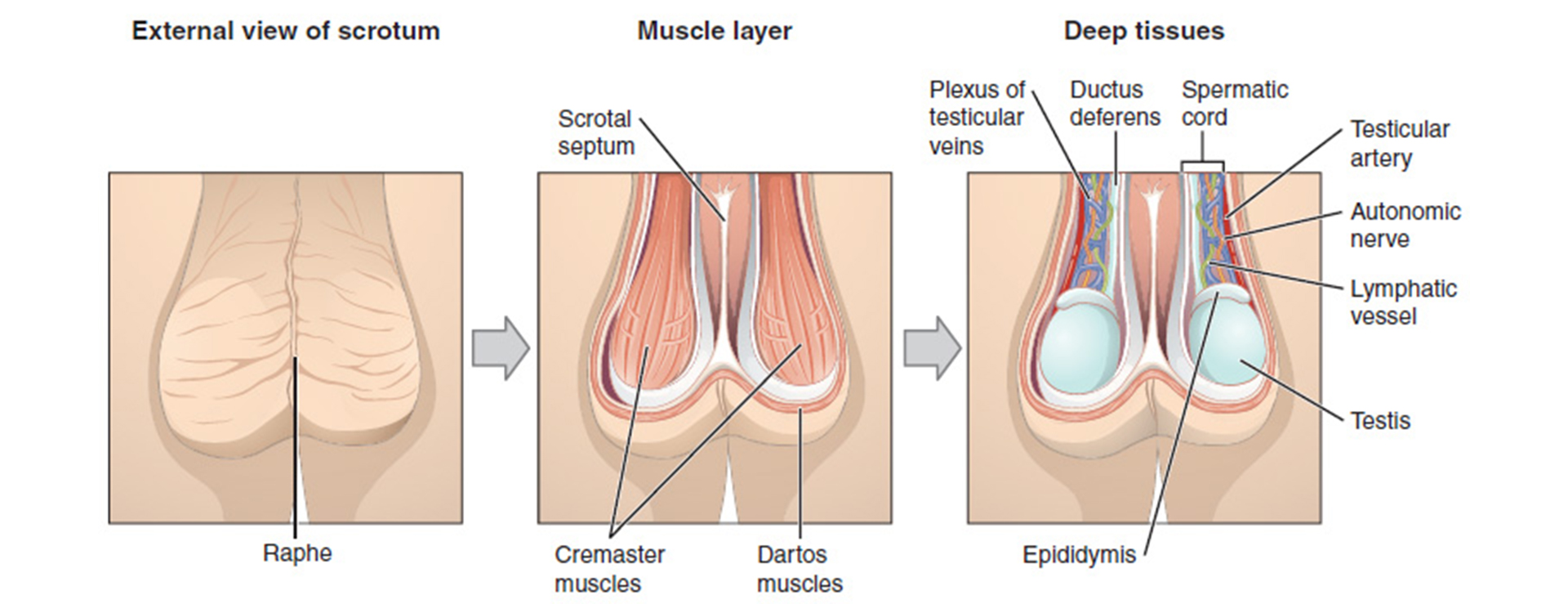
How does Mumps spread to the Testes?
Once the Mumps virus has entered the host body, it will multiply in the respiratory tract and mainly affect the Parotid glands, as discussed above. The symptoms usually stay limited to these glands only, and the disease resolves on its own without any treatment. But if the disease persists, it may cause complications in other parts of the body, like coverings of the brain, pancreas, and testes.
One-fourth of the infected males in the post-puberty age complain of swelling and pain in the testicles caused by the Mumps virus. While it may resolve on its own in some cases, anyone experiencing symptoms should take it seriously.