#265 AI-powered real-time annotations during RAPN- Dr. Joan Sureda, Dr. Ketan Badani, Dr. L. Zuluaga
This is one of the 2023 KS International Innovation Awards videos selected for inclusion in the Vattikuti Foundation – ORSI Humans on the Cutting Edge of Robotic Surgery Conference, October 6, 7 & 8, 2023 in Ghent, Belgium. Posting does not imply that is has been selected as a Finalist, just that the content will be discussed at the Conference.
From the entry: Title: AI-powered real-time annotations during RAPN
Authors:
Laura Zuluaga1, Ketan K. Badani1
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York Corresponding Author: Ketan K. Badani, MD
Department of Urology
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
Address: 1425 Madison Avenue, 6th Floor New York City, NY, 10029, USA
Office: +1 (212) 241-3919
Fax: +1 (212) 987-4675
Mail: ketan.badani@mountsinai.org
Abstract Word Count: 1864/2030 Number of Tables: 1 Number of Graphics: 1 Keywords: Robotics, Category: SURGICAL TECHNOLOGY & SIMULATION – Instrumentation & Technology – Training & Skills Assessment
Introduction and Objective The potential of real-time artificial intelligence (AI) annotation in the surgical field lies in its ability o automatically extract valuable information from surgical videos. This extracted content holds potential applications in surgical education and qualitative initiatives. In this groundbreaking development, we showcase the pioneering use of AI in urologic robotic surgery, capturing live surgical video of a robotic-assisted partial nephrectomy (RAPN) and providing real-time annotations for key surgical steps and safety milestones.
71
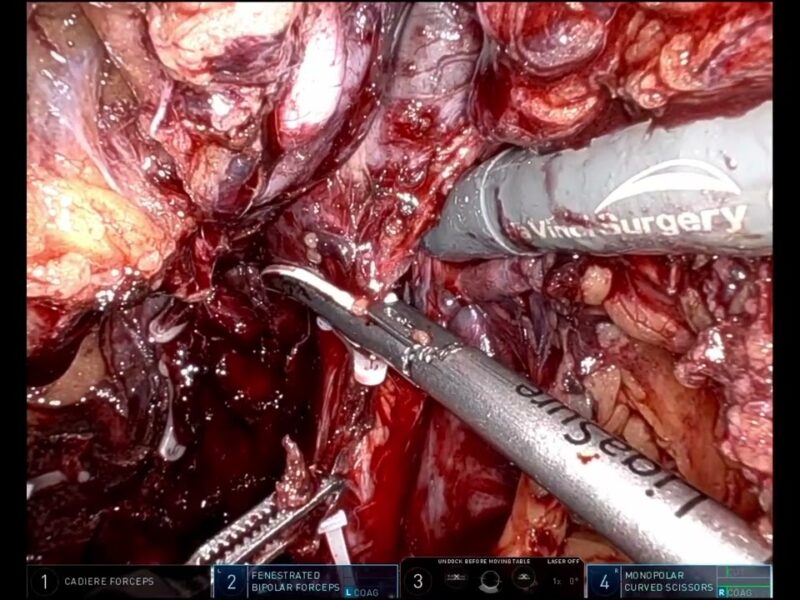
Methods We conducted an educational symposium, which broadcasted a live robotic-assisted partial nephrectomy (RAPN). A surgical AI platform system (Theator, Palo Alto, CA) generated real-time annotations and identified operative safety milestones (Image 1). By using Video Transfer Network and capturing clips in full context, this system enables automatic recognition and surgical mapping, providing real-time insights into the surgical process.
57
Results Real-time AI annotations for the procedure are found in Table 1. Safety milestones included deliberate views of structures such as the gonadal vessels and the ureter. AI annotated surgical events included intraoperative ultrasound, temporary clip application and removal, hemostatic powder application, and notable hemorrhage.
43
Conclusions Surgical intelligence successfully showcased real-time AI annotations of two separate urologic robotic procedures during a live telecast for the first time. This AI model allows notification of critical steps in developing surgery, thus avoiding unwanted outcomes and correcting potential intraoperative risk maneuvers. We consider this a first step in real-time intraoperative decision support, potentially improving surgical outcomes and supporting training and education. Total:232
Table 1. Description of system annotations for Robotic Assisted Partial Nephrectomy
System annotations
Robotic Asssisted Partial Ne phre ctomy
Steps Annotations Preparation Adhesiolysis Dissection and mobilization Lesion resection Resection site closure Final inspection Safety Milestones View of gonadal vein View of ureter Surgical Events Intraoperative ultrasound (*2) Temporary clip application Temporary clip removal Hemostatic powder application (*2) Notable hemorrhage Hemostatic suture Specimen packaging
See more at: https://vattikutifoundation.com/videos/
Date
August 15, 2020