Robot Assisted Partial Nephrectomy in Ectopic Pelvic Kidney
This video was entered by Dr. Akshay Bhandari in the 2022 KS International Robotic Surgery Innovation Awards, sponsored by the Vattikuti Foundation. It was featured in the Vattikuti Symposium ‘Humans at the Cutting Edge of Robotic Surgery,’ held in Miami, Florida November 19, 2022.
Here is the Abstract:
Robot Assisted Partial Nephrectomy in Ectopic Pelvic Kidney
Surgeon: Dr. Akshay Bhandari MD
Submission preparation: Diana M Lopategui MD, Nicole Matluck MD, Akshay Bhandari MD
Introduction: Pelvic kidneys result from an incomplete or aberrant ascent during embryologic development. They present special treatment challenges due to a greater risk of injury of aberrant vessels or abdominal viscera.
Case Presentation: A 69 year old male was referred to our clinic for evaluation of incidental finding on a CT scan: a 4.1cm enhancing exophytic mass in a pelvic kidney, and duplication of the infrarenal inferior vena cava. Patient elected to undergo a robot assisted laparoscopic partial nephrectomy.
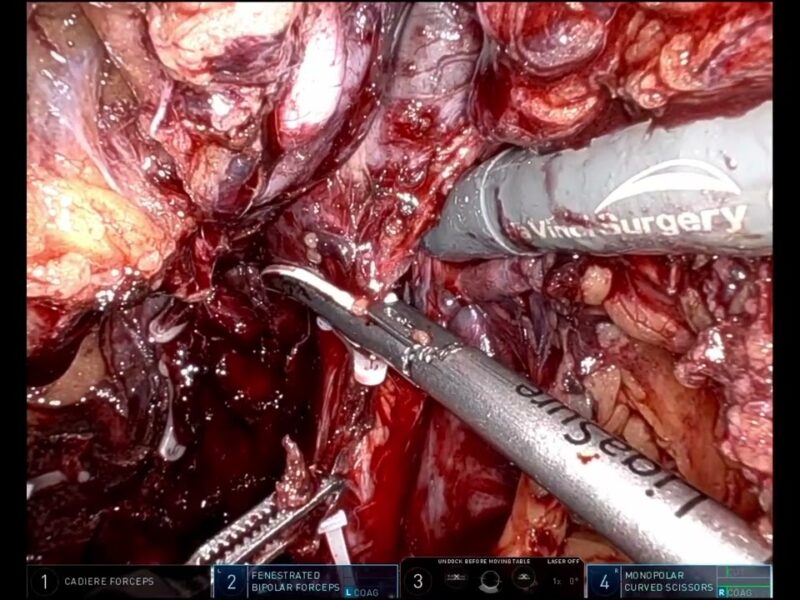
Procedure: Patient was positioned supine in steep Trendelenburg. Four 8mm robotic trocars were placed higher in the abdomen in pelvic surgery placement, as well as additional 12mm and 5mm assistant trocars. Monopolar scissors, bipolar grasper and tip up fenestrated grasper were used to reflect the colon off the kidney. Hilar structures were carefully isolated. The surface of the mass was exposed entirely, confirming its location with intraoperative ultrasound. Main and accessory renal arteries were clamped, and mass was excised entirely. Resection bed, Gerota and surgical incisions were closed in the standard fashion.
Outcomes: Total clamp time was 8 minutes. Post operative course was uncomplicated and patient was discharged on post-operative day one. Pathology showed a 4.5cm papillary renal cell carcinoma tumor.
Conclusion: Robotic assisted partial nephrectomy can be achieved in complex anatomy by adhering to basic surgical principles, including adequate preoperative imaging and planning, meticulous dissection of the hilum and the use of intraoperative ultrasound.
See more at: vattikutifoundation.com/videos
Date
August 15, 2020