SAFE (Saline-Assisted Fascial Exposure) for Nerve-Sparing during RARP
This video was entered by Dr. Ashutosh Tewari in the 2022 KS International Robotic Surgery Innovation Awards, sponsored by the Vattikuti Foundation. It was featured in the Vattikuti Symposium ‘Humans at the Cutting Edge of Robotic Surgery,’ held in Miami, Florida November 19, 2022.
Full Title:
SAFE (Saline-Assisted Fascial Exposure) for Nerve-Sparing during Robotic-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy (RARP)
During a radical prostatectomy, the urologist faces the challenge of balancing the risk of extracapsular extension (ECE) and the preservation of the neural hammock. Despite great improvement in anatomic and functional knowledge over the last two decades as well as refinement of surgical techniques with the introduction of robotic-assisted surgery, erectile dysfunction (ED) continues to be an important concern with reported rates between 20% and 70% after 12 months of follow-up. Moreover, ED is linked to depression and distress that may have a serious impact on patients` and partners’ quality of life and well-being.
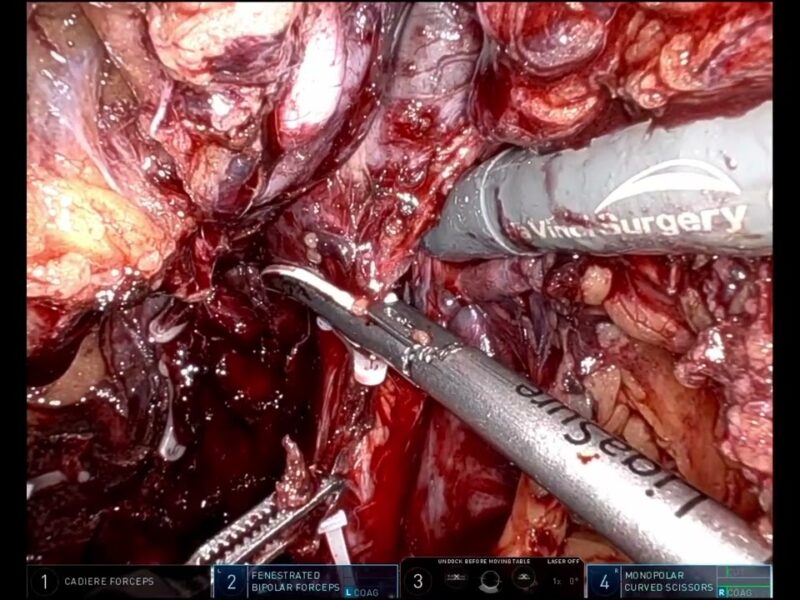
We have developed the SAFE technique to optimize erectile function after RARP through a less traumatic release of the neurovascular bundle. Normal saline was selected given its osmolality and theoretical decreased risk of neuropraxia. This technique is applied to patients with an increased risk of ECE depending on Martini’s nomogram prediction1.
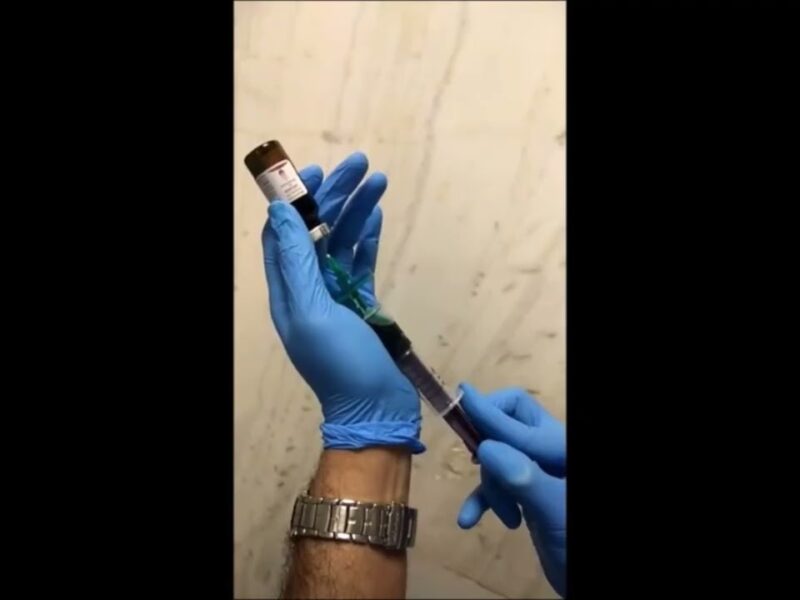
The SAFE technique is performed once the surgeon has done an early release of the neurovascular bundle. Under direct vision and using the right assistant port, a transperitoneal 23 Gauge x 3/4 ” butterfly needle is introduced to inject 30 cc of saline solution in between the layers of the periprostatic fascia. The injection is carried out until engorgement or ballooning of the tissue is observed. Advantages of the technique: Facilitates an atraumatic dissection of the multilayer periprostatic fascia, promoting the visualization of the neurovascular hammock. It is a harmless procedure, easy to implement in clinical practice.
1. Martini A, Cumarasamy S, Haines KG, Tewari AK. An updated approach to incremental nerve sparing for robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. BJU Int. 2019;124(1):103-108. doi:10.1111/bju.14655
See more at: vattikutifoundation.com/videos
Date
August 15, 2020