563 Robot-Assisted Intercostal Nerve Harvesting: Advancing Donor Nerve Surgery
Dr. Philippe Liverneaux
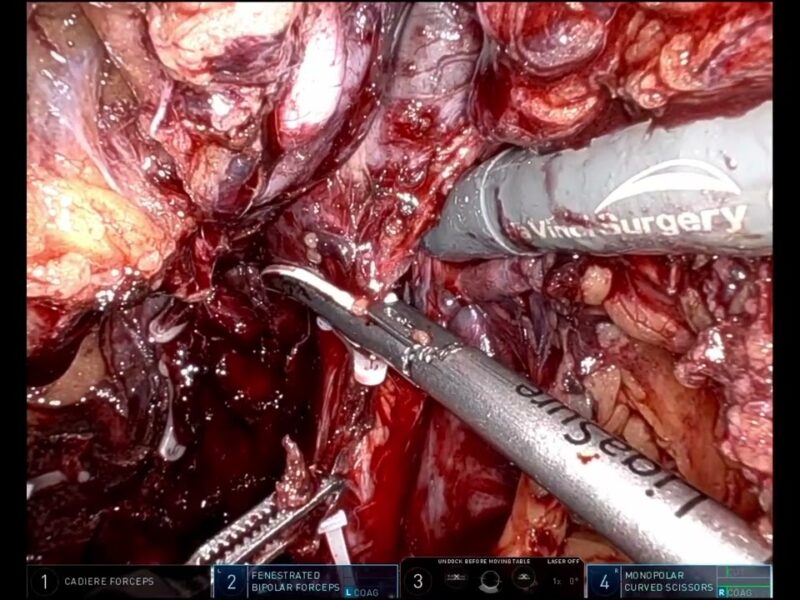
Intercostal nerves are frequently used as donors in brachial plexus reconstruction, yet conventional harvesting requires large thoracic incisions, leading to trauma and perioperative risks. Thoracoscopic techniques reduce invasiveness but remain limited by prolonged operative time and restricted instrument precision. This study illustrates the feasibility of robot-assisted intercostal nerve harvesting as a minimally invasive alternative. Using the Da Vinci® robotic system, nerves were isolated through three thoracic ports with CO₂ insufflation ensuring field stability. Enhanced 3D vision and tremor-free instruments improved surgical accuracy. In porcine models, the fourth to sixth intercostal nerves were harvested successfully with intact thoracic structures, minimal blood loss, and an average operative time of 70 minutes. Early clinical cases confirmed safety and efficacy, demonstrating shorter incisions, reduced trauma, and fewer complications compared with traditional approaches. Robot-assisted harvesting thus enables precise nerve isolation, lowers morbidity, and holds potential to redefine donor nerve surgery in brachial plexus reconstruction. Orthopedic Surgery, Procedure Innovation
See more at: https://vattikutifoundation.com/videos/
Date
August 15, 2020