Robotic Lateral Pelvic LND for Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer
From KS Awards entry abstract:
ROBOTIC LATERAL PELVIC NODE DISSECTION FOR LOCALLY ADVANCED RECTAL CANCER
Introduction: Lateral pelvic node dissection in rectal cancer is a controversial topic. In select cases it may be beneficial when combined with neoadjuvant treatment. More than a third of rectal cancer cases in India are locally advanced and a significant proportion is formed by young patients. Hence exploring new techniques and routes to achieve optimal oncosurgical outcomes while preserving the sexual and urinary functions is necessary when it comes to lateral pelvic node clearance, especially in narrow male pelvis.
Here we have demonstrated the feasibility of lateral pelvic node dissection in a locally advanced rectal cancer using da Vinci Xi robotic platform.
Case Details: This is a 36 year old gentleman with a rectal adenocarcinoma starting 2cm from the anal verge. It was non metastatic but MRI showed gross invasion anteriorly into the prostatic stroma, along with bilateral lateral pelvic lymphadenopathy. He received neoadjuvant chemoradiation. Post neoadjuvant therapy he was taken up for total pelvic exenteration with bilateral lateral pelvic node clearance.
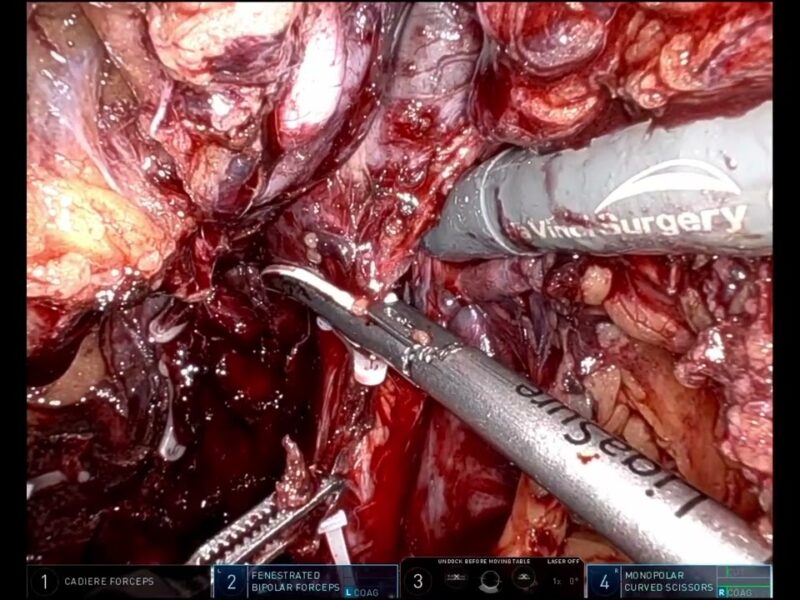
Surgical details: the port positioning was not different from the standard robotic rectal cancer resections. Here the nodal clearance was completed before the excision of the primary tumor. We prefer to address the lateral zone first and then move on to the medial zone.
The margins of the lateral zone dissection were identified first i.e. external iliac vessels and obturator internus laterally, vessels arising from internal iliac artery medially, confluence of internal and external iliac vessels posteriorly. Ureter was medialized. The fibrofatty tissue containing the nodes was dissected and finally reflected off the obturator nerve.
For the medial zone, the margins are: medially pelvic hypogastric plexus, laterally vessels arising from internal iliac vessels, posteriorly presacral space. Gentle dissection prevents handling and injury to the plexus. In this case the dissection was carried down much below the inferior vesical artery since the patient was planned for exenteration. The nodal tissue is carefully separated from the vessels arising from internal iliac artery.
Operative time for each side: 30 minutes, blood loss: minimal.
Conclusion: Robotic lateral pelvic node clearance is feasible and can be done safely. DaVinci Xi platform give excellent visualization and maneuverability to carry out the procedure in narrow pelvis and bulky tumors with minimal blood loss.
Narrated robotic surgery video, with photo showing optimal port placement and da Vinci Xi robotic surgery camera footage, 07:50
Date
August 15, 2020